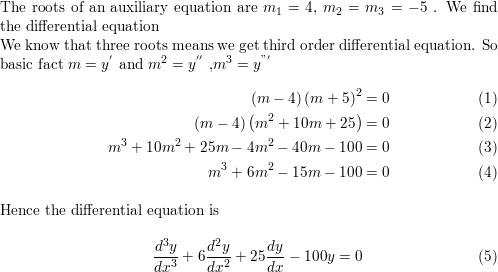SOLVED: Two roots of a cubic auxiliary equation with real coefficients are m = -2, and mz = l + 1. What is the corresponding homogeneous linear differential equation? Discuss: is your

BIM-based method calculation of auxiliary materials required in housing construction - ScienceDirect
![Cost balance and auxiliary equations for all system components [3,13,14]. | Download Scientific Diagram Cost balance and auxiliary equations for all system components [3,13,14]. | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/371815877/figure/tbl3/AS:11431281170103445@1687609774495/Cost-balance-and-auxiliary-equations-for-all-system-components-3-13-14.png)
Cost balance and auxiliary equations for all system components [3,13,14]. | Download Scientific Diagram

Application of Linear ODE as Auxiliary Equation to the Nonlinear Evolution Equation : Science and Education Publishing

How to find roots of auxiliary equation in calculator | Differential equations casio fx 991ms #1 - YouTube
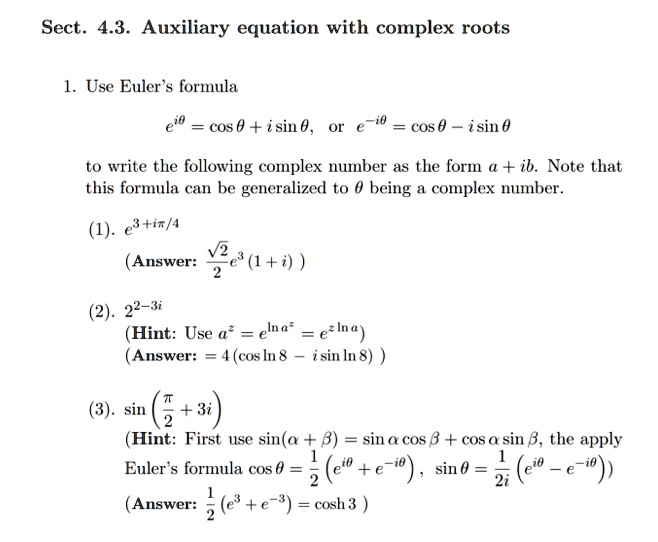
SOLVED: Sect: 4.3. Auxiliary equation with complex roots 1. Use Euler's formula cos 0 + i sin 0, cos 0 + i sin 0 to write the following complex number in the

Source data and auxiliary calculation results in MS Excel Source: Model... | Download Scientific Diagram

Differential Equations Solved Examples: The roots of an auxiliary equation are: m = 2 +- 3i , 5 , -5 , 1 Write the corresponding homogeneous differential equation using differential operator notation.
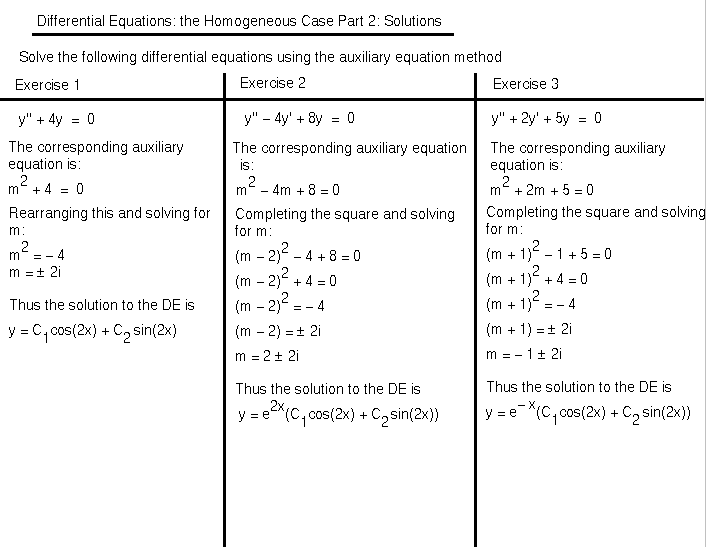
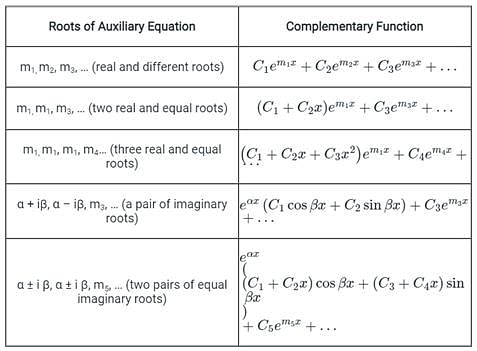
Differential Equations - MATH100 Revision Exercises - Resources - Mathematics and Statistics - University of Canterbury - New Zealand

vi) The auxiliary equation of the lines represented by ( 6 x ^ { 2 } + k x y + y ^ { 2 } = 0 ) is ( m ^ { 2 } + k m + 6 = 0 ) since one of the line is ( 2 x + y = 0 ) whose slope is ( m = - 2 )

![Auxiliary equations for the Matrix [A] | Download Table Auxiliary equations for the Matrix [A] | Download Table](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/267156112/figure/tbl6/AS:392105236156425@1470496581287/Auxiliary-equations-for-the-Matrix-A.png)